Median Nerve Palsy Hand | The median nerve, colloquially known as the eye of the hand, is one of the three major nerves of the forearm and hand. Distal median nerve injury causes palsy of the lumbricals i and ii with preserved function of extrinsic flexors. Clinical features of ulnar nerve palsy. Anatomy of median nerve palsy. Claw hand median nerve dr.
The median nerve is one of the major peripheral nerves of the upper limb, originating from the brachial plexus. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus. It controls abduction of the thumb, flexion of hand at wrist, flexion of digital phalanx of the fingers. Anatomy of median nerve palsy. Injuries such as a supracondylar fracture, elbow dislocationor any form of fracture should be examined for damage to.

Median nerve palsy also affects the appearance of the hand when the patient is trying to make a fist. In this article, we shall look at its anatomical course, motor and motor functions. Claw hand median nerve dr. Median nerve lesions thumb is externally rotated into plane of palm. It courses from the brachial plexus in the axilla to innervate the intrinsic muscles of the hand. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus. Ulnar nerve palsy (incomplete claw hand) подробнее. The median nerve innervates the muscle in the front side of. Median nerve palsy abductor pollicis brevis ring finger flexor digitorum superficialis thumb metacarpophalangeal joint opponensplasty. In the hand, the median nerve divides into two branches: Median nerve lesions, carpal tunnel syndrome, ulnar nerve lesions, claw hand, radial nerve lesions. There is loss of flexion of the second and third digits due to loss of the lumbrical motor innervation. Weakness of pinch grip (due to involvement of flexor pollicis longus and flexor digitorum profundus of.
Anatomy of median nerve palsy. In this article, we shall look at its anatomical course, motor and motor functions. Related online courses on physioplus. Distal median nerve injury causes palsy of the lumbricals i and ii with preserved function of extrinsic flexors. Tendon transfer in median nerve injuries median nerve palsy is perhaps the most devastating single nerve injury of the upper extremity.

High median nerve palsy that presents with: Distal median nerve injury causes palsy of the lumbricals i and ii with preserved function of extrinsic flexors. It is the only nerve that passes through the carpal. In this article, we shall look at its anatomical course, motor and motor functions. Sidey}, journal={the lancet}, year={1955}, volume={265}, pages={971} }. The median nerve controls the majority of the muscles in the forearm. Tendon transfer in median nerve injuries median nerve palsy is perhaps the most devastating single nerve injury of the upper extremity. Clinical features of ulnar nerve palsy. Paralysis of flexor digitorum radialis will result in lateral deviation of the hand, loss of flexion at the interphalangeal joints due to paralysis of the flexor digitorum superficialis, and flexor digitorum profundus. Median nerve is one of the major nerves of the forearm and hand, it arises from the brachial plexus (a network of nerves from lower cervical to the first thoracic that supplies the upper limb) in the axilla passes to the elbow, forearm and hand. There is loss of flexion of the second and third digits due to loss of the lumbrical motor innervation. Numbness over hypothenar eminence and ulnar distribution of hand. Conclusion early tendon transfer has a unique role in the management of median nerve palsy hand and we suggest this procedure should be considered in both high and low lesions.
Tendon transfers are often used in patients with the median nerve may get damaged during surgery to parts of the arm or hand. This can be from a fracture or other traumatic injury, or compression from excess fluid build up following an injury. Ulnar nerve palsy (incomplete claw hand) подробнее. Distal median nerve injury causes palsy of the lumbricals i and ii with preserved function of extrinsic flexors. Median nerve exploration was performed in 4 cases and was supplemented by a tendon transfer for thumb opposition.
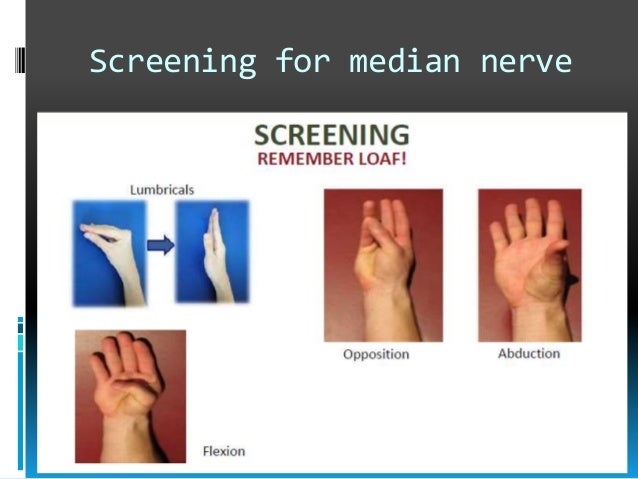
Palsies of the median nerve may be acute, requiring urgent intervention or chronic, indicating a more conservative approach. Clinical features of ulnar nerve palsy. In the hand, the median nerve divides into two branches: It courses from the brachial plexus in the axilla to innervate the intrinsic muscles of the hand. Median nerve is one of the major nerves of the forearm and hand, it arises from the brachial plexus (a network of nerves from lower cervical to the first thoracic that supplies the upper limb) in the axilla passes to the elbow, forearm and hand. Inability to oppose and abduct the thumb. The recurrent motor branch of the median nerve and the digital cutaneous branch of the median nerve. The median nerve is one of the major peripheral nerves of the upper limb, originating from the brachial plexus. Distal median nerve injury causes palsy of the lumbricals i and ii with preserved function of extrinsic flexors. The median nerve innervates the majority of the muscles in the anterior forearm , and some intrinsic hand muscles. Clinical examination methods including entrapment neuropathy of median nerve. Anatomy of median nerve palsy. Not only is there a loss of fine motor control and opposition, but sensibility is lost over the area of the hand used for precision movements and prehensile.
Median nerve lesions thumb is externally rotated into plane of palm median nerve palsy. Injuries to the arm, forearm or wrist area can lead to various nerve disorders.
Median Nerve Palsy Hand: The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb.
